Lithium battery packs, as the cornerstone of energy storage systems, are typically composed of multiple batteries connected in series or parallel. However, discrepancies in manufacturing, aging rates, and temperature variations can lead to inconsistencies in voltage and capacity among single cells. These imbalances can significantly affect the overall performance, lifespan, and safety of the battery pack.
Moreover, during idle periods, the chemical reactions within lithium batteries cause a gradual loss of charge. This self-discharge characteristic further exacerbates imbalances between batteries, posing additional challenges to the battery system.
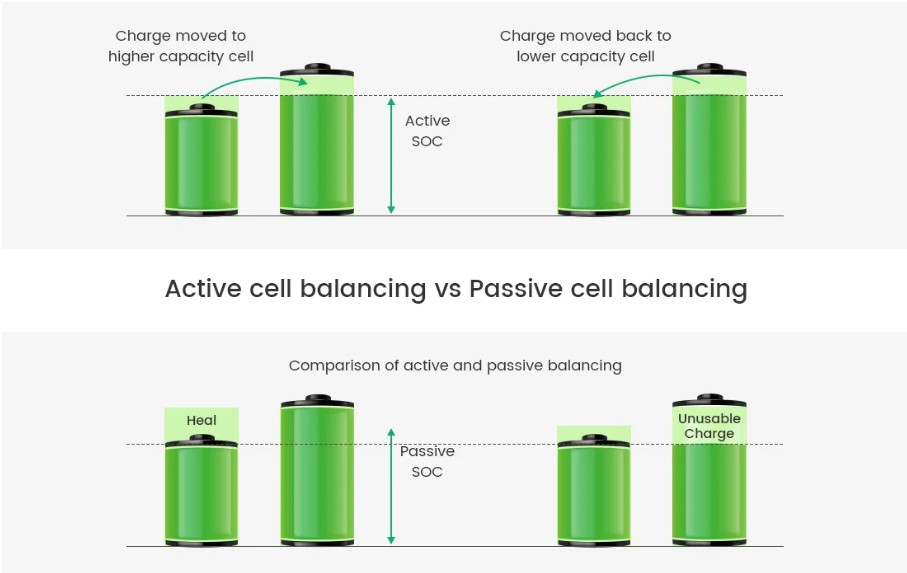
Addressing these challenges requires advanced battery balancing strategies and robust management systems to optimize the performance and safety of lithium battery pack BMS. These strategies are categorized into two primary types: passive balancing and active balancing.
Passive balancing involves discharging the excess energy from higher-voltage cells through resistors, converting the surplus energy into heat to bring cell voltages into balance. This is the most common balancing method due to its low cost and straightforward implementation. However, the effectiveness of passive balancing is often constrained by the capacity of the lowest-performing battery in the pack, leading low energy utilization efficiency and significant heat loss.
Active balancing redistributes energy from higher-energy cells to lower-energy ones through charge transfer. This approach typically relies on inductors, transformers, or capacitors as energy storage components, significantly improving energy efficiency. Active balancing is well-suited for large-capacity, high-series battery systems. However, its complexity in circuit design, higher hardware requirements, and associated costs make it more suitable for high-performance applications.
The Battery Management System (BMS) is the core control unit of a lithium battery pack, tasked with real-time monitoring and management of each cell’s operational status to ensure performance and safety. The BMS plays a critical role in battery balancing by offering the following advantages:
The Gerchamp G-BS for ESS ensures stable operation of lithium battery packs by continuously monitoring key parameters such as battery voltage, temperature, and current. Its advanced balancing capabilities maximize efficiency, with the G-BMU module supporting intelligent cell-level balancing control, which, avoids interference with cell voltage and temperature data acquisition.